
 神经到神经酸
神经到神经酸

 神经酸前瞻性研究
神经酸前瞻性研究

 回顾研究
回顾研究


树突-Dendritic
神经系统在人体内主要是负责传输和接受的信息。神经元作为神经系统的主要细胞,能感知环境的变化,神经信息从树突接收后再将信息传递给其他的神经元,并指令集体做出反应。神经元占了神经系统约一半,其他大部分由胶质细胞所构成。神经胶质细胞不会产生电脉冲。它们维持体内稳态,形成髓鞘,并为神经元提供支持和保护。

髓鞘-Myelin Sheath
中枢系统中的髓鞘是由寡突胶质细胞(Oligodendrocyte)或其它类型的神经支持细胞形成的,其中70%是由各类脂质所组成,包裹在神经细胞轴突外面,提供保护和支持。
目前知道髓鞘的功能大致可分为三种:
1. 支持轴突与周围组织,例如相邻的轴突之间的电气绝缘,以避免信息传输干扰;
2. 提供“跳跃式传导”(Saltatory Conduction)的机制来加快动作电位的传递;
3.是在一些轴突受损的情况下引导轴突的再生。

神经酸-Nervonic Acid
神经酸(Nervonic Acid, 学名:顺-15-二十四碳单烯酸),别名鲨鱼酸。是大脑神经细胞和神经组织的核心天然成分之一,是生物膜的重要组成物质也是髓鞘形成的中间产物。神经酸是迄今为止世界上发现的能促进受损神经组织修复,是神经细胞特别是大脑细胞、视神经细胞、周围神经生长、再发育和维持的必须“高级营养素”在大脑中的鞘磷脂大约占据40%的脂肪酸,而神经酸占鞘磷脂的36% (成年人)。据目前研究,神经酸在大脑中是调节脑细胞膜正常功能,达到维持神经系统的保护作用。
参考文献:
Fan et al. 2018. Biosynthesis of nervonic acid and perspectives for its production by microalgae and other microorganisms. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8859-y
内容:
Nervonic acid (NA) is a major very long-chain monounsaturated fatty acid found in the white matter of mammalian brains, which plays a critical role in the treatment of psychotic disorders and neurological development. In the nature, NA has been synthesized by a handful plants, fungi, and microalgae. Although the metabolism of fatty acid has been studied for decades, the biosynthesis of NA has yet to be illustrated. Generally, the biosynthesis of NA is considered starting from oleic acid through fatty acid elongation, in which malonyl-CoA and long-chain acyl-CoA are firstly condensed by a rate-limiting enzyme 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase (KCS). Heterologous expression of kcs gene from high NA producing species in plants and yeast has led to synthesis of NA. Nevertheless, it has also been reported that desaturases in a few plants can catalyze very long-chain saturated fatty acid into NA. This review highlights recent advances in the biosynthesis, the sources, and the biotechnological aspects of NA.
参考文献:
Lewkowicz, N, et al. (2019). Naturally Occurring Nervonic Acid Ester Improves Myelin Synthesis by Human Oligodendrocytes. Cells, 8(8), 786. doi.org/10.3390/cells8080786
内容(摘要):
少突胶质细胞(oligodendrocytes)的功能障碍被认为是多发性硬化症中髓鞘再生效率低下的主要原因之一,导致疾病逐渐进展。少突胶质细胞来源于少突胶质前体细胞 (oligodendrocyte progenitor cells),它们填充成人中枢神经系统,但它们对髓鞘合成的生理功能是有限的。人类饮食中用于鞘磷脂合成的必需脂质摄入量低可能是脱髓鞘增加和髓鞘再生过程效率降低的原因。在我们对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎大脑脂质谱的研究中,我们发现在急性炎症期间,神经酸合成被抑制,这是将常见底物的脂质代谢途径转变为促炎性花生四烯酸产生的结果。在体外成熟少突胶质细胞前体细胞 (human model of maturating oligodendrocyte precursor cells) 的人体模型实验中,我们证明鱼油混合物 (fish oil mixture) 影响成熟少突胶质细胞前体细胞的功能,导致髓鞘碱性蛋白、髓鞘少突胶质细胞糖蛋白和蛋白脂蛋白的合成得到改善,以及鞘磷脂。此外,还证明鱼油混合物可减少促炎细胞因子和趋化因子,并增强成熟少突胶质细胞前体细胞的成纤维细胞生长因子 2 (fibroblast growth factor 2) 和血管内皮生长因子 (vascular endothelial growth factor) 合成。基于这些观察,我们提出摄入富含神经酸酯的鱼油混合物可以改善少突胶质细胞的功能,影响少突胶质前细胞成熟并限制炎症。
参考文献:
王性炎 & 王姝清.(2010).神经酸研究现状及应用前景. 中国油脂(03),1-5. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZYZZ.0.2010-03-002.
内容(摘要):
神经酸是大脑神经细胞和神经组织的核心天然成分, 是促进受损神经细胞和组织修复、再生的特殊物质。了解神经酸的化学结构、生物合成途径、药理作用以及应用研究现状, 对开发应用神经酸产品具有重要意义。世界各国政府和科学家都十分关注神经酸的开发与应用, 随着传统神经酸资源的短缺和限制, 从植物油中发掘神经酸是一条可持续发展之路 。
参考文献:
王性炎,谢胜菊 & 王高红.(2018).中国富含神经酸的元宝枫籽油应用研究现状及前景. 中国油脂(12),93-95+104. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZYZZ.0.2018-12-022.
内容(摘要):
神经酸是大脑神经细胞和神经组织中的核心天然成分,有特殊的生理功能和药理作用。元宝枫籽油是中国独有资源,其富含神经酸。为了促进元宝枫籽油的开发利用研究,综述了中国元宝枫籽油的应用研究现状和前景。元宝枫籽油对人体健康特别是脑健康的有益作用已引起我国医学界的重视,具有重要深度开发价值。
参考文献:
Li, et al. 2019. A mini review of nervonic acid: Source, production, and biological functions. J. Foodchem. 301, 125286.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125286
内容:
Nervonic acid (NA) has attracted considerable attention because of its close relationship with brain development. Sources of NA include oil crop seeds, oil-producing microalgae, and other microorganisms. Transgenic technology has also been applied to improve the sources and production of NA. NA can be separated and purified by urea adduction fractionation, molecular distillation, and crystallization. Studies on NA functionality involved treatments for demyelinating diseases and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, as well as prediction of mortality due to cardiovascular diseases and chronic kidney disease. This mini review focuses on the sources, production, and biological functions of NA and provides prospective trends in the investigation of NA.
参考文献:
Qiuyue Ma, et al. 2020. The Acer truncatum genome provides insights into nervonic acid biosynthesis. Plant J. 104(3):662-678
内容(摘要):
Acer truncatum (purpleblow maple) is a woody tree species that produces seeds with high levels of valuable fatty acids (especially nervonic acid). However, the lack of a complete genome sequence has limited both basic and applied research on A. truncatum. We describe a high-quality draft genome assembly comprising 633.28 Mb (contig N50 = 773.17 kb; scaffold N50 = 46.36 Mb) with at least 28 438 predicted genes. The genome underwent an ancient triplication, similar to the core eudicots, but there have been no recent whole-genome duplication events. Acer yangbiense and A. truncatum are estimated to have diverged about 9.4 million years ago. A combined genomic, transcriptomic, metabonomic, and cell ultrastructural analysis provided new insights into the biosynthesis of very long-chain monounsaturated fatty acids. In addition, three KCS genes were found that may contribute to regulating nervonic acid biosynthesis. The KCS paralogous gene family expanded to 28 members, with 10 genes clustered together and distributed in the 0.27-Mb region of pseudochromosome 4. Our chromosome-scale genomic characterization may facilitate the discovery of agronomically important genes and stimulate functional genetic research on A. truncatum. Furthermore, the data presented also offer important foundations from which to study the molecular mechanisms influencing the production of nervonic acids.
参考文献:
Manuela M. et al. 1998. Fatty Acid Composition of Human Brain Phospholipids During Normal Development. J. Neurochem. 71, 2528-2533.
内容(摘要):
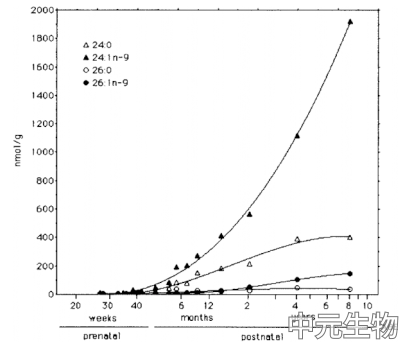
对22例人前脑磷脂酰亚胺(PE)、乙醇胺原生质(EPs)、磷脂酰丝氨酸(PS)、磷脂酰喹啉(PC)和鞘磷脂的脂肪酸组成进行了研究。在PE和PC中,二十二碳六烯酸(22:6n-3)随年龄增长而增加,而花生四烯酸(20:4n-6)则保持不变。在EP中,22:6n-3的增加幅度小于20:4n-6,肾上腺素(22:4n-6)和油酸(18:ln-9)是产后主要的脂肪酸。鞘磷脂是一种典型的髓磷脂,主要由长链饱和脂肪酸和单不饱和脂肪酸组成。其中以神经酸(24∶ln-9)为主链脂肪酸在SP中依次为24:0、26:1 n-9、26:0,其在出生后的增加是显著的。
人类发育中的前脑中的脂肪酸,以nmol/g的形式表达,与年龄成图(对数刻度)。与之前图中的PuFAs长链不饱和脂肪酸相比,所有四种脂肪酸都显示出从大约足月开始逐渐增加,并与髓鞘形成的时间相一致。利用三次多项式方程,得到了这种曲线增长的最佳拟合。n-9家族的结果显示了脑Sp中两种油酸产物24:1n -9(神经酸)和26:ln-9的发育变化。为了进行比较,我们在图中添加了它们的饱和对应物24:0(木质素酸)和26:0(谷氨酸),它们也是髓鞘磷脂的典型代表。可见,神经酸是迄今为止最重要的Sp中较长脂肪酸,其在髓鞘形成过程中积累最快。
参考文献:
王性炎,谢胜菊 & 王高红.(2018).中国富含神经酸的元宝枫籽油应用研究现状及前景. 中国油脂(12),93-95+104. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZYZZ.0.2018-12-022.
内容(摘要):
神经酸是大脑神经细胞和神经组织中的核心天然成分,有特殊的生理功能和药理作用。元宝枫籽油是中国独有资源,其富含神经酸。为了促进元宝枫籽油的开发利用研究,综述了中国元宝枫籽油的应用研究现状和前景。元宝枫籽油对人体健康特别是脑健康的有益作用已引起我国医学界的重视,具有重要深度开发价值。

